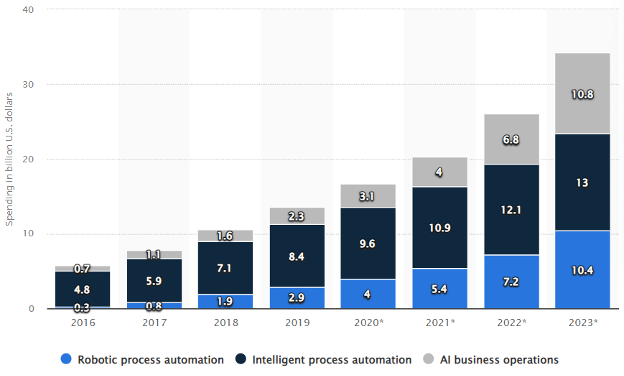
Today, we are making large leaps toward automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Therefore, investment in this tech has also increased. Statistics from 2023 indicate that executives globally allocated more than $34.2 billion toward automation and AI operations.
Source: Statista
This substantial increase, compared to the modest $5.8 billion expenditure in 2016, showcases a transformative mindset within organizations, recognizing the potential of automation to revolutionize various aspects of operations.
COOs across the globe are now actively seeking innovative solutions to enhance workflow efficiency and reduce reliance on manual tasks. A particularly important path that has gained momentum is RPA – a revolutionary technology that changes how organizations address their organizational work and processes.
Definition of Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
As the digital transformation age takes shape with internal operation technologies and customer support systems attuning themselves to automation, RPA has become a prominent tool in improving productivity.
At its core, RPA is a technological innovation designed to emulate human interactions with software, performing high-volume, repeatable tasks efficiently. RPA achieves this through the creation of software programs or bots, enabling them to log into applications, input data, execute calculations, and improve operations in applications or workflows.
The adaptability of RPA extends beyond task automation. When combined with AI, machine learning, and IoT, COOs can make the most out of RPA’s foundational functions for more complex processes. For example, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) has been used to facilitate the interpretation of text or handwriting, while Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables the extraction of entities such as names or addresses.
Additionally, machine vision is further allowing operations bots to interpret images, contributing to more nuanced automation capabilities in operations.
COOs Augmenting RPA’s Capabilities
The growing popularity of RPA emanates from its potential to cut costs, streamline processes, and elevate customer experiences. Notably, RPA is accessible to business units without extensive training or IT support, allowing organizations to make the most out of automation without significant alterations to their existing IT infrastructure.
However, as the adoption of RPA becomes widespread, COOs are recognizing the need to seamlessly integrate RPA process automations into their IT systems. While RPA significantly accelerates processes previously handled by humans, COOs understand that there are several challenges as well that need to be addressed before applying it to interfaces or process workflows.
Modern RPA platforms have acknowledged these challenges, integrating AI, machine vision, and natural language processing to enhance adaptability and scalability.
Integrating Process Mining and AI Modules in RPA
Enterprises are increasingly turning to process mining and task mining tools to enhance their RPA implementations. Process mining tools automatically capture business process workflows, creating templates for RPA automations.
These tools analyze logs from Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications to generate a map of common enterprise processes. Task mining tools, on the other hand, use machine vision to capture user interactions across multiple applications.
Major RPA vendors are actively developing integrations with process mining tools, recognizing their potential to streamline RPA implementations. This integration allows for a more comprehensive understanding of existing workflows, facilitating smoother automation transitions.
Additionally, RPA tools can be connected to AI modules, incorporating capabilities like OCR, machine vision, natural language understanding, or decision engines. This amalgamation, termed intelligent process automation, offers advanced features packaged into cognitive automation modules tailored to specific industries or business processes.
Real-Time Applications Across Different Industries
RPA has found utility across diverse industries, particularly those involving repetitive tasks. For example, in financial operations, RPA has automated several aspects of the operational workflow, such as:
- Governance,
- Account reconciliation,
- Entry management
- Initial and basic audits
- Accounts preparation
- Ratio analysis,
- After-sales service support,
- Invoice processes, and more.
Meanwhile, telecommunications providers are using RPA to configure new services and run billing systems as well as equipment failures.
These applications focus on enabling the acceptance of best practices within particular segments, demonstrating that RPA can be implemented in any industry.
RPA Advantages in Digital Transformation
The inclusion of RPA in the operational structure of an organization can make a serious contribution to COO’s digital transformation path. Several benefits highlight RPA’s impact on reshaping business operations:
- Enhanced Customer Service: RPA plays a key role in automating contact center tasks, including e-signature verification, document uploads, and information verification. This contributes to more efficient and responsive customer service.
- Regulatory Compliance: RPA ensures that business operations and processes align with regulations and compliance standards. The technology’s ability to digitize and audit process data facilitates adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Accelerated Processing Time: One of the major strengths shown by RPA is its capacity to considerably shorten processing time. RPA can now execute tasks that were previously cumbersome and time-consuming.
- Improved Efficiency: RPA improves operational efficiency by digitalizing and auditing the process data. Manual and repetitive activities are minimized so that the workers can pay more attention to strategic work value-added activities.
- Cost Reduction: They can also reduce their costs by making as few manual and repetitive functions possible.
- Employee Productivity: RPA enables employees to be more productive by automating routine tasks. This allows employees to redirect their efforts towards tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and executive decision-making.
Challenges & Considerations
Despite its transformative potential, RPA is not without its challenges, necessitating a careful approach to governance and implementation:
- Scalability Issues: Enterprises often face challenges in scaling RPA initiatives. While RPA bots are relatively easy to implement, their governance and management can be quite complex, hindering seamless scalability.
- Automation Limitations: Critics argue that RPA software tools primarily focus on automating individual tasks, requiring additional effort to integrate multiple tasks into a cohesive process. Organizations must understand these limitations to fully leverage RPA’s capabilities.
- Security Concerns: RPA bots may need access to sensitive information to complete tasks, posing additional security risks if compromised. Ensuring robust security measures is imperative to protect against potential threats.
- Resiliency Challenges: Ensuring such operational continuity in an unexpected change of circumstances becomes one focal object RPA governance.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Requirements: The introduction of RPA requires new QA practices to ensure that bots continue to function in the right manner. QA becomes an integral part of RPA governance to maintain operational efficiency.
- Privacy Considerations: RPA bots might handle personally identifiable information subject to privacy regulations. Adhering to data protection laws, such as GDPR, requires organizations to implement measures that guarantee the lawful processing of sensitive information.
- Efficiency Comparison: While RPA bots replicate human interactions, some argue that automating applications through APIs or workflow automations within applications might be more efficient. Assessing the most effective automation method becomes crucial for organizations.
Sectors Seeing RPA Integration
The versatility of RPA translates into diverse applications by COOs and other operations executives across various industries:
- Customer Service: In customer service, RPA proves instrumental in automating contact center tasks, including signature verification, document uploads, and information verification.
- Accounting: Organizations leverage RPA in accounting for tasks such as general accounting, operational accounting, transactional reporting, and budgeting.
- Financial Services: The financial services industry harnesses RPA for foreign exchange payments, automating account operations, managing audit requests, and processing insurance claims.
- Healthcare: Within the healthcare sector, RPA streamlines processes related to patient records, claims processing, customer support, account management, billing, reporting, and analytics.
- Human Resources
- Supply Chain Management
As these integrate automation software, a transformation in job roles is inevitable. While certain jobs may be replaced, new opportunities will emerge for individuals responsible for maintaining and improving RPA software. C-level executives shoulder the responsibility of ensuring that business objectives are achieved and emerging governance policies align with RPA tools deployment.
With the incorporation of RPA, leadership roles also change where either CTO or CIO takes an active position. As far as their responsibilities are concerned, they become accountable for business results and risks associated with the deployment of RPA tools.
Collaboration among the Chief Operating Officer (COO), CIO, Chief Human Resources Officer, and relevant C-level executives is essential to establish a secure platform for controlling and operating bots across systems.
Conclusion
In business operations, the incorporation of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) stands out as a transformative force for COOs. As the role of COOs evolves, RPA presents a key solution for bringing together automation, AI, and IoT applications.
As RPA finds applications across industries, its benefits in enhancing customer service, ensuring regulatory compliance, accelerating processing time, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling employee productivity become evident.
Organizations utilizing RPA are not merely adopting a technology but making the most out of a shift in how work is executed. They are essentially laying the foundation for a future where humans and automation coexist synergistically.


0 Comments